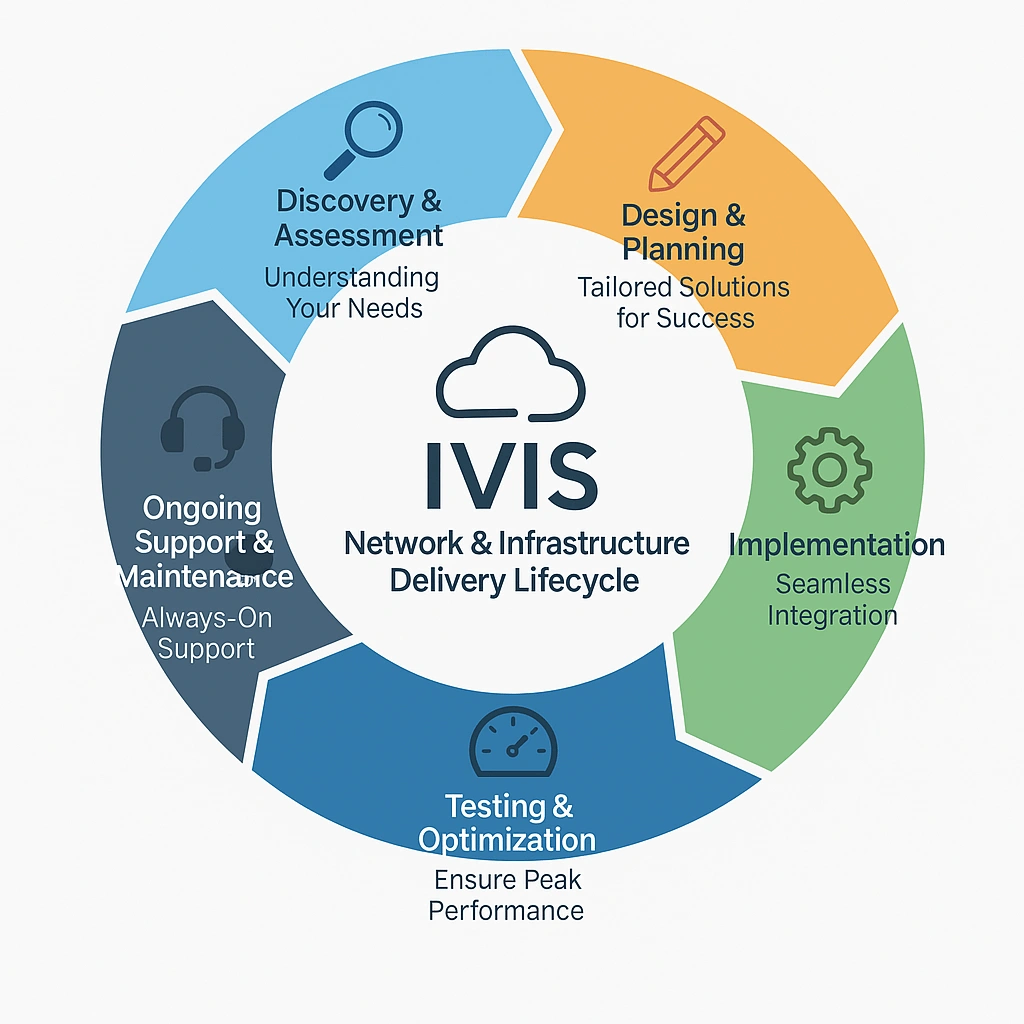
Network Engineering
Network Engineering refers to the design, implementation, management, and optimization of an organization's communication systems. This includes the creation of wired and wireless networks that connect devices, systems, and users across different locations. Network engineers focus on the reliability, speed, and security of these connections.
Key Components:
• Network Design: Creating network topologies and blueprints for the structure of communication systems within an organization.
• Routing & Switching: Configuring and optimizing routers, switches, and other networking hardware to ensure efficient and secure data traffic management.
• Security: Implementing firewalls, VPNs, intrusion detection systems (IDS), and encryption to secure data transmission and prevent unauthorized access.
• Network Optimization: Ensuring that the network operates at peak efficiency, with minimal latency and maximum bandwidth, often through traffic management and optimization techniques.
• Wireless Networking: Designing and deploying Wi-Fi networks that meet the needs of the organization, ensuring coverage, security, and speed.
Benefits:
• Improved Communication: Facilitates seamless communication and data transfer across different parts of the organization.
• Enhanced Security: Protects sensitive data and network connections from cyber threats.
• Scalability: Designs networks that can scale with organizational growth.
Infrastructure Engineering
Infrastructure Engineering involves the development and maintenance of the physical and virtual systems that support IT operations. It encompasses the hardware, software, and network systems that provide the foundation for all technological functions within a company.
Key Components:
• Data Centers: Designing and managing data centers that house servers, storage devices, and networking hardware critical for running business applications and services.
• Server & Storage Management: Implementing and managing server hardware, cloud storage, and virtualized environments to ensure the business’s IT resources are always available and scalable.
• Cloud Computing: Implementing cloud-based infrastructures for increased flexibility, scalability, and cost-efficiency in managing IT resources.
• Virtualization: Creating virtual versions of physical devices, such as servers, storage, and networks, to optimize resource utilization, reduce costs, and improve disaster recovery.
• Disaster Recovery & Backup: Designing systems that ensure data is regularly backed up, and critical services can be restored rapidly after any unforeseen disruptions or disasters.
Benefits:
• High Availability: Ensures business systems and services are up and running 24/7 with minimal downtime.
• Cost Efficiency: Optimizes resources and reduces hardware costs through virtualized environments and cloud computing.
• Scalability: Infrastructure can grow with the business, supporting expanding data, applications, and services.